The channel is being held off because the SHARE_CLK signal is low. The open drain SHARE_CLK signal is a bi-directional open drain coordination signal used between devices to enforce time=zero and time delay synchronization.
NOTE: The 'Why am I Off?' tool may provide additional insights.
Device Behavior for VIN and SHARE_CLK
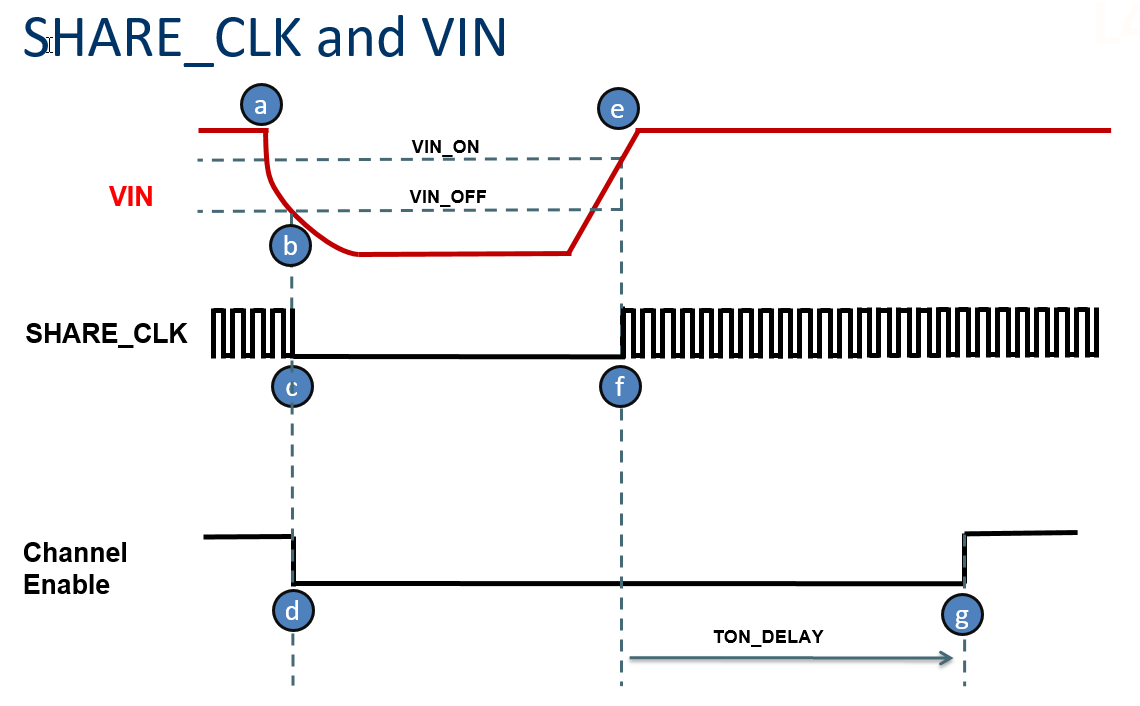
The example waveform above illustrates the behavior of a the SHARE_CLK signal in response to VIN, and the behavior of device channels in response to SHARE_CLK stopping and restarting. The example starts with the device in normal operating mode with no faults. Typically the SHARE_CLK signal is connected between PSM devices to insure coherent sequencing. Let's take the scenario where VIN for the system is removed and then re-applied. The behavior of the system is as describe in the following sequence points highlighted above:
- a – The system is operating normally, with VIN good and no faults. SHARE_CLK is toggling normally to provide a common arbitrated timebase across devices for sequencing.
- b -- A device in the system detects that its VIN voltage drops below its programmed VIN_OFF threshold.
- c – The first such device to see VIN drop below VIN_OFF immediately holds SHARE_CLK low to signal to the system that VIN was lost, and a normal power down should occur
- d -- When a channel (of any device connected to the common SHARE_CLK) detects that the SHARE_CLK has stopped, it immediately disables its output
- For PSM Controllers, power deliver is stopped by the controller itself
- For PSM Managers, the output enable (VOEN) pin is de-asserted to disable the managed power supply
- e -- VIN ramps back up. Devices detect when VIN rises above their programmed VIN_ON threshold, and release the common SHARE_CLK.
- f – When the last such device in the system detects VIN rising above its programmed VIN_ON threshold, it releases the common SHARE_CLK signal and the SHARE_CLK starts toggling again. Devices connected to SHARE_CLK detect that SHARE_CLK has started, and initiate a coordinated re-sequence (the start of SHARE_CLK marks time=zero).
- f – During the coordinated re-sequence, each channel, after waiting its programmed on delay (TON_DELAY) will start ramping its voltage up
- Controllers have the ability to ramp the voltage directly, and will ramp the output consistent with the programmed TON_RISE setting.
- Managers will assert the assert the VOEN pin to enable the managed supply at this time
This coordination feature insures that as power is applied (or lost) the system remains coordinated in its sequencing behavior, and all devices agree on time=zero for up sequencing, and turn off immediately when VIN is lost.
Possible Causes:
- Missing or wrong pullup, preventing SHARE_CLK from toggling properly. Consult the datasheet for proper pullup selection.
- Missing board connection (cracked or missing 0 ohm resistor to common SHARE_CLK, board/assembly error, etc)
- One or more PSM devices in the system are holding SHARE_CLK low
- They may be in RESET, or
- Their VIN may be below their programmed VIN_ON threshold.
- An external device (for example an unprogrammed FPGA) is holding SHARE_CLK low
Remedies and Workarounds
Here are some experiments you can try to narrow things down:
- Configure the channel to ignore the FAULTB pin in the "Fault Sharing" Section of the configuration. This will allow the channel to startup up regardless of the pin.
- To determine if the 'root cause' is a PSM device or external source (unprogrammed FPGA, etc) driving the pin low:
- Disable propagation to FAULTB/GPIOB for all devices in the system
- If the FAULTB pin remains low, this indicates an external device or circuit may be keeping the pin low.
- If the DRC check produces any warnings, fix these and see if the problem goes away.
Other Debugging Tips
If the channel is presently off, use the "Why am I Off? Tool". Otherwise, if you have an oscilloscope, do the following:
- Trigger the scope on the falling edge of the FAULTB pin and
- Look at other possible signals in the system that may be responsible driving FAULTB low
- Disable fault propagation for all devices. If the pin is still low, trace the schematic for any devices connected to the pin and insure they are not driving it low.